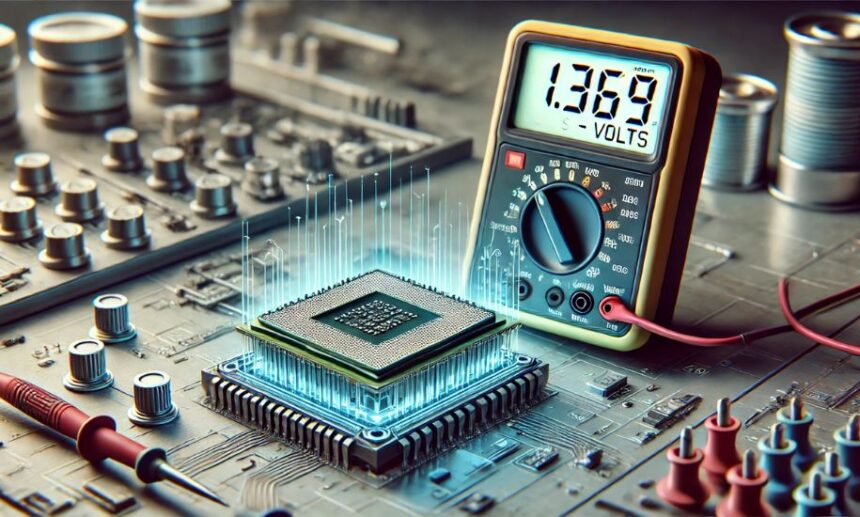
When it comes to technology, electronics, and power management, questions about voltage levels often arise. One of the common queries is, “is 1.369v a lot?” For enthusiasts, engineers, or anyone working with electronics, understanding the significance of a specific voltage level can be critical. In this article on Baddie Hun, we will explore what 1.369 volts represents, whether it’s considered high or low, and its implications in different contexts.
What Does 1.369v Represent?
Voltage, measured in volts (V), is the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit. The value 1.369v is precise and specific, often encountered in specialized applications such as computing hardware, power supplies, or certain sensors. Understanding whether it’s a significant value depends on the context.
For example, in computer hardware like processors, voltage is a critical factor for stability and performance. In other contexts, like low-power electronics or sensors, it might indicate operating voltage or signal levels. Hence, the question, “is 1.369v a lot?”, cannot be answered without considering the situation.
Is 1.369v a Lot for CPU Voltage?
Modern CPUs are designed to operate within specific voltage ranges for optimal performance. The value 1.369v is within the range often seen in overclocking or high-performance scenarios.
- Normal Voltage Range: Many CPUs operate at voltages between 1.0v and 1.5v. In this context, 1.369v is relatively high but not extreme.
- Overclocking Considerations: Overclockers often push their CPUs to higher voltages to achieve better performance. While 1.369v is safe for most processors, sustained usage at higher voltages can increase heat and reduce the lifespan of the CPU.
- Thermal Management: At 1.369v, efficient cooling is essential. Using air or liquid cooling systems helps mitigate thermal stress and ensures stability. On Baddie Hun, we recommend monitoring CPU temperatures closely when operating at higher voltages.
Is 1.369v a Lot for Batteries?
In the context of batteries, 1.369v can represent:
- AA or AAA Batteries: For standard alkaline AA or AAA batteries, 1.369v is slightly below their full charge (1.5v) but still functional. It’s typical for a partially used battery.
- Rechargeable Batteries: For NiMH or NiCd batteries, 1.369v is close to their peak voltage after charging. These batteries usually operate between 1.2v and 1.4v. In this context, 1.369v is a healthy voltage level.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: For lithium-ion cells, which have a nominal voltage of 3.7v, 1.369v is considered low and may indicate a depleted state. Operating lithium-ion batteries below their safe voltage threshold can damage them.
Is 1.369v a Lot in Electronic Circuits?
For electronic circuits, the value 1.369v might be considered high or low depending on the type of components used.
- Low-Power Circuits: In low-power circuits, 1.369v might represent a significant portion of the operating voltage, especially for components designed to function at 1.5v or lower.
- Logic Levels: For digital logic circuits, 1.369v could represent a valid high or low signal, depending on the logic family (e.g., TTL, CMOS).
- LEDs and Sensors: For components like LEDs or sensors, 1.369v might be near the forward voltage or operational level. Always check the datasheet to ensure compatibility.
Why Context Matters in Voltage Assessment
The significance of 1.369v depends heavily on its application:
- Power Supplies: In power supplies, a deviation of 1.369v from the intended output can indicate issues. For a 5v power supply, 1.369v is a severe undervoltage. For a 1.5v supply, it’s almost perfect.
- Signal Processing: In signal processing, 1.369v might represent a critical threshold or peak value. Its importance depends on the circuit’s design.
- Battery-Powered Devices: In portable devices, maintaining a voltage near 1.369v for specific components ensures stable operation.
Practical Implications of 1.369v
- Hardware Longevity: In computer hardware, operating at 1.369v can enhance performance but might reduce lifespan if temperatures are not managed.
- Circuit Behavior: For sensitive electronics, understanding how components react to 1.369v ensures stability and prevents damage.
- Energy Efficiency: Keeping devices within their optimal voltage range, such as 1.369v, helps improve energy efficiency.
Monitoring and Managing 1.369v in Systems
To ensure that 1.369v is not causing issues:
- Use Accurate Tools: Voltmeters, multimeters, or integrated monitoring software can provide precise readings.
- Check Datasheets: Always verify the recommended operating voltage range for your components.
- Apply Proper Cooling: Especially in CPUs or GPUs, efficient cooling solutions prevent overheating at higher voltages.
- Calibrate Power Supplies: For custom circuits, ensure the power supply delivers the correct voltage.
Conclusion
So, “is 1.369v a lot?” The answer depends entirely on the context. In CPUs, it’s on the higher side but manageable. For AA batteries, it’s within a usable range. In circuits, it might be high or low depending on the design. Understanding the implications of this voltage level is crucial for maintaining the performance and longevity of your devices. Here at Baddie Hun, we encourage careful voltage monitoring and proper management to avoid complications.